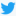


John Davison Rockefeller, Jr. was a major philanthropist and a pivotal member of the prominent Rockefeller family. He was the sole son among the five children of businessman and Standard Oil industrialist John D. Rockefeller and the father of the five famous Rockefeller brothers. In biographies, he was invariably referred to as "Junior" to distinguish him from his more celebrated father, known as "Senior".
Early life
Rockefeller, Jr. was the fifth and last child of John D. Rockefeller (July 8, 1839 – May 23, 1937) and his wife, Laura Celestia Spelman. Living in his father's mansion at 4 West 54th Street he attended Park Avenue Baptist Church at 64th Street (now Central Presbyterian Church), and the Browning School, a tutorial establishment set up for him and other children of associates of the family; it was located in a brownstone owned by the Rockefellers, on West 55th Street.
Initially he had intended to go to Yale but was encouraged by William Rainey Harper, president of the University of Chicago, among others, to enter the Baptist-oriented Brown University instead. Nicknamed Johnny Rock by his roommates, he joined both the Glee and the Mandolin Clubs, taught a Bible class and was elected junior class president. Scrupulously careful with money, he stood out as different from other rich men's sons.
In 1897 he graduated with the degree of Bachelor of Arts, after taking nearly a dozen courses in the social sciences, including a study of Karl Marx's Das Kapital. He joined the Alpha Delta Phi fraternity, and was elected to Phi Beta Kappa.
Business career
After graduation, Rockefeller, Jr. joined his father's business (October 1, 1897) and set up operations in the newly-formed family office at Standard Oil's headquarters at 26 Broadway. He became a Standard Oil director; he later also became a director in J. P. Morgan's U.S. Steel company, which had been formed in 1901. After a scandal involving the then head of Standard Oil, John Dustin Archbold (the successor to Senior), and bribes he had made to two prominent Congressmen, unearthed by the Hearst media empire, Junior resigned from both companies in 1910 in an attempt to "purify" his ongoing philanthropy from commercial and financial interests.
In April, 1914, after a long period of industrial unrest, the Ludlow massacre occurred at the coal-mining company, Colorado Fuel and Iron (CFI). Junior owned a controlling interest in the company (40% of its stock) and sat on the board as an absentee director. Twenty men, women and children died in the incident and Junior was subsequently called to testify in January, 1915, before the US Commission on Industrial Relations. He was at the time being advised by William Lyon MacKenzie King and the pioneer public relations expert, Ivy Lee. Junior also at this time met with the union organizer, Mary Harris "Mother" Jones and admitted fault in his testimony. MacKenzie King was later to say that this testimony was the turning point in Junior's life, restoring the reputation of the family name; it also heralded a new era of industrial relations in the country (see below).
During the Great Depression he developed and was the sole financier of a vast 14-building real estate complex in the geographical center of Manhattan, Rockefeller Center, and as a result became one of the largest real estate holders in New York City. He was influential in attracting leading blue chip corporations as tenants in the complex, including GE and its then affiliates RCA, NBC and RKO, as well as Standard Oil of New Jersey (Esso), and Associated Press and Time Inc, as well as branches of the then Chase National Bank, now JP Morgan Chase.
The family office, of which he was in charge, called now formally "Rockefeller Family and Associates" (and informally, Room 5600), shifted from Standard Oil headquarters to the 56th floor of what is now the landmark GE Building, upon its completion in 1933.
In 1921, he received about 10% of the shares of the Equitable Trust Company from his father, making him the bank's largest shareholder. Subsequently, in 1930, the Equitable merged with the Chase National Bank, now JP Morgan Chase, and became at that time the largest bank in the world. Although his stockholding was reduced to about 4% following this merger, he was still the largest shareholder in what became known as the "Rockefeller bank". As late as the 1960s his family still retained about 1% of the bank's shares, by which time his son David had become the bank's president.
In the late 1920s, Rockefeller founded the Dunbar National Bank in Harlem. The financial institution was located within the Paul Laurence Dunbar Apartments at 2824 Eighth Avenue near 150th Street and serviced a primarily African American clientele. It was unique among New York City financial institutions in that it employed African Americans as tellers, clerks, bookkeepers and in key management positions. However, the bank folded after only a few years of operation.
Philanthropy and social causes
In a celebrated letter to Nicholas Murray Butler in June, 1932, subsequently printed on the front page of The New York Times, Rockefeller, Jr., a lifelong teetotaler, argued against the continuation of the Eighteenth Amendment on the principal grounds of an increase in disrespect for the law. This letter became the singular event that pushed the nation to repeal Prohibition.
However, Rockefeller, Jr. is most remembered for his philanthropy, giving over $537 million to myriad causes over his lifetime. He created the Sealantic Fund in 1938 to channel gifts to his favorite causes; previously his main philanthropic organization had been the Davison Fund. He had become the Rockefeller Foundation's inaugural president in May, 1913 and proceeded to dramatically expand the scope of this institution, founded by his father. Later he would become involved in other organizations set up by Senior, the Rockefeller University and the International Education Board.
In the social sciences, he founded the Laura Spelman Rockefeller Memorial in 1918, which was subsequently folded into the Rockefeller Foundation in 1929. A committed internationalist, he financially supported programs of the League of Nations and crucially funded the formation and ongoing expenses of the Council on Foreign Relations and its initial headquarters building, in New York in 1921.
In 1900, after he had earlier (1896) persuaded his father to support nascent cancer research, Rockefeller money built a medical laboratory on the campus of Cornell Medical Center. This subsequently became Memorial Hospital, which decades later became the world renowned Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.
He established the Bureau of Social Hygiene in 1913, a major initiative that investigated such social issues as prostitution and venereal disease, as well as studies in police administration and support for birth control clinics and research. In 1924, at the instigation of his wife, he provided crucial funding for Margaret Sanger in her pioneering work on birth control and involvement in population issues.
In the arts, he gave extensive property he owned on West Fifty-fourth Street for the site of the Museum of Modern Art, which had been co-founded by his wife in 1929.
In November, 1926, Rockefeller came to the College of William and Mary for the dedication of an auditorium built in memory of the organizers of Phi Beta Kappa, the honorary scholastic fraternity founded in Williamsburg in 1776. Rockefeller was a member of the society and had helped pay for the auditorium. He had visited Williamsburg the previous March, when the Reverend Dr. W.A.R. Goodwin escorted him — along with his wife Abby, and their sons, David, Laurance, and Winthrop — on a quick tour of the city. The upshot of his visit was that he approved the plans already developed by Goodwin and launched the massive historical restoration of Colonial Williamsburg on November 22, 1927. Amongst many other buildings restored through his largesse was The College of William & Mary's Wren Building.
Through negotiations by his son Nelson, in 1946 he bought for $8.5 million - from the major New York real estate developer William Zeckendorf - and then donated the land along the East River in Manhattan upon which the United Nations headquarters was built. This was after he had vetoed the family estate at Pocantico as a prospective site for the headquarters (see Kykuit). Another UN connection was his early financial support for its predecessor, the League of Nations; this included a gift to endow a major library for the League in Geneva which today still remains a resource for the UN.
A confirmed ecumenicist, over the years he gave substantial sums to Protestant and Baptist institutions, ranging from the Interchurch World Movement, the Federal Council of Churches, the Union Theological Seminary, the Cathedral of St. John the Divine, New York's Riverside Church and the World Council of Churches. He was also instrumental in the development of the research that led to Robert and Helen Lynd's famous Middletown studies work that was conducted in the city of Muncie, Indiana, that arose out of the financially supported Institute of Social and Religious Research.
As a follow on to his involvement in the Ludlow Massacre, Rockefeller was a major initiator with his close friend and advisor William Lyon Mackenzie King in the nascent industrial relations movement; along with major chief executives of the time he incorporated Industrial Relations Counselors (IRC) in 1926, a consulting firm whose main goal was to establish industrial relations as a recognized academic discipline at Princeton University and other institutions. It succeeded through the support of prominent corporate chieftains of the time, such as Owen D. Young and Gerard Swope of General Electric.
Overseas philanthropy
In the 1920s he also donated a substantial amount towards the restoration and rehabilitation of major buildings in France after World War I, such as the Rheims Cathedral, the Château de Fontainebleau and the Château de Versailles, for which in 1936 he was awarded France's highest decoration, the Grand Croix of the Légion d'honneur (subsequently also awarded decades later - in 2000 - to his son, David Rockefeller).
He also liberally funded the notable early excavations at Luxor in Egypt, and the American School of Classical Studies for excavation of the Agora and the reconstruction of the Stoa of Attolos, both in Athens; the American Academy in Rome; Lingnan University in China; St. Luke's International Hospital in Tokyo; the library of the Imperial University in Tokyo; and to the Shakespeare Memorial Endowment at Stratford-on-Avon.
In addition, he provided the funding for the construction of the Palestine Archaeological Museum in East Jerusalem - the Rockefeller Museum - which today houses many antiquities and was the home of many of the Dead Sea Scrolls till they were moved to the Shrine of the Book at the Israel Museum.[18]
Conservation
He had a special interest in conservation, and purchased and donated land for many American National Parks, including Grand Teton (hiding his involvement and intentions behind the Snake River Land Company), Acadia, Great Smoky Mountains, Yosemite, and Shenandoah. In the case of Acadia National Park, he financed and engineered an extensive Carriage Road network throughout the park. Both the John D. Rockefeller, Jr. Memorial Parkway that connects Yellowstone National Park to the Grand Teton National Park and the Rockefeller Memorial in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park were named after him. He was also active in the movement to save redwood trees, making a significant contribution to Save-the-Redwoods League in the 1920s to enable the purchase of what would become the Rockefeller Forest in Humboldt Redwoods State Park.
In 1951, he established Sleepy Hollow Restorations, which brought together under one administrative body the management and operation of two historic sites he had acquired: Philipsburg Manor House in North Tarrytown, now called Sleepy Hollow, (acquired in 1940 and donated to the Tarrytown Historical Society), and Sunnyside, Washington Irving’s home, acquired in 1945. He bought Van Cortland Manor in Croton-on-Hudson in 1953 and in 1959 donated it to Sleepy Hollow Restorations. In all, he invested more than $12 million in the acquisition and restoration of the three properties that were the core of the organization’s holdings. In 1986, Sleepy Hollow Restorations became Historic Hudson Valley, which also operates the current guided tours of the Rockefeller family estate of Kykuit in Pocantico Hills.
He is the author of the noted life principle, among others, inscribed on a tablet facing his famed Rockefeller Center: "I believe that every right implies a responsibility; every opportunity, an obligation; every possession, a duty".
In 1935, Rockefeller received The Hundred Year Association of New York's Gold Medal Award, "in recognition of outstanding contributions to the City of New York." He was awarded the Public Welfare Medal from the National Academy of Sciences in 1943.
Wives, children and legacy
In August 1900, Rockefeller was invited by the powerful Senator Nelson W. Aldrich of Rhode Island to join a party aboard President William McKinley's yacht, the Dolphin, on a cruise to Cuba. Although the outing was of a political nature, Rockefeller's future wife Abby Greene Aldrich was included in the large party; the two had been courting for over four years.
Junior married Abby Greene Aldrich on October 9, 1901, in what was seen at the time as the consummate marriage of capitalism and politics. Moreover, their wedding was the major social event of its time - one of the most lavish of the Gilded Age. It was held at the Aldrich Mansion at Warwick Neck, Rhode Island, and attended by Standard Oil and other great industrial executives of the age.
The couple had six children, a daughter and the five Rockefeller brothers:
Abby Rockefeller Mauzé (November 9, 1903 - May 27, 1976)
John D. Rockefeller III (March 21, 1906 - July 10, 1978)
Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 - January 26, 1979)
Laurance Spelman Rockefeller (May 26, 1910 - July 11, 2004)
Winthrop Rockefeller (May 1, 1912 - February 22, 1973)
David Rockefeller (born June 12, 1915)
Abby Rockefeller died of a heart attack at the family apartment at 740 Park Avenue in April, 1948. Junior remarried in 1951, to Martha Baird Allen, the widow of his old college classmate, Arthur Allen. Rockefeller died of pneumonia on May 11, 1960 at the age of 86, and was interred in the family cemetery in Tarrytown, with 40 family members present.
His sons, the five Rockefeller brothers established an unparalleled network of social connections and institutional power over time, based on the foundations that Junior - and before him Senior - had laid down. David became an internationally renowned banker, philanthropist and world statesman. John D. III became a major philanthropist and internationalist. Laurance became a significant venture capitalist and major conservationist. Nelson and Winthrop Rockefeller later became state governors; Nelson went on to become Vice President of the United States under Gerald Ford.
Residences
Junior's principal residence in New York was the 9-story mansion at 10 West Fifty-fourth Street, but he owned a group of properties in this vicinity, including Nos 4, 12, 14 and 16 (some of these properties had been previously acquired by his father, John D. Rockefeller). After vacating Number 10 in 1936, these properties were razed and subsequently all the land was gifted to his wife's Museum of Modern Art. In that year he moved into a luxurious 40-room triplex apartment at 740 Park Avenue. In 1953, the real estate developer William Zeckendorf bought the 740 Park Avenue apartment complex and then sold it to Rockefeller, who quickly turned the building into a cooperative, selling it on to his rich neighbors in the building.
Years later, just after his son Nelson, as Governor of New York State, helped foil a bid by greenmailer Saul Steinberg to take over Chemical Bank, Steinberg bought Junior's apartment for $225,000, $25,000 less than it had cost new in 1929. It has since been called the greatest trophy apartment in New York, in the world's richest apartment building.
John Davison Rockefeller, Jr. (JDR Jr.) was a philanthropist who gave more than $537 million to educational, religious, cultural, medical, and other charitable projects. The son of John D. Rockefeller, founder of the Standard Oil Company, and Laura Spelman Rockefeller, he was born in Cleveland, Ohio, on January 29, 1874, and died in Tucson, Arizona, on May 11, 1960. He had four sisters, one of whom died in infancy. In 1897 he graduated with the degree of Bachelor of Arts from Brown University, where he was member of Alpha Delta Phi and was elected to Phi Beta Kappa.
On October 9, 1901, he married Abby Greene Aldrich, whose father was U.S. Senator Nelson W. Aldrich of Rhode Island. Six children were born to the couple: a daughter, Abby, and five sons, John D. 3rd, Nelson A., Laurance S., Winthrop and David Rockefeller.
Abby Aldrich Rockefeller died in 1948. On August 15, 1951, JDR Jr. married Mrs. Martha Baird Allen, a former concert pianist and the widow of Arthur M. Allen, a classmate at Brown University and a close friend.
Imbued with a deep sense of stewardship, John D. Rockefeller, Jr. believed that his inherited fortune should be used for the public good. Recent estimates of his net worth at various times during his life place it at $995 million in 1928, $379.6 million a decade later, and $336.5 million in 1950; his net worth in 1928 is estimated to have been the equivalent of $6.5 billion in 1988 dollars. But rather than a career in business, Rockefeller devoted his life primarily to philanthropic and civic activities, particularly to those designed to advance human welfare and to further international, interfaith and interracial concepts. Among his gifts were large sums to educational organizations, religious causes, hospitals, scientific projects, conservation and parklands, and historic preservation. He was responsible for the restoration of Colonial Williamsburg in Virginia, and he donated the land along the East River in Manhattan for the site of the United Nations headquarters.
WORK WITH HIS FATHER
After graduating from Brown, JDR Jr. entered his father's office at 26 Broadway in New York and worked closely with his father and his principal advisor, the Rev. Frederick T. Gates, in the business, philanthropic, and civic undertakings of the family. He also worked to extend those civic and philanthropic efforts. In 1950 he paid tribute to his father before the Chamber of Commerce of the State of New York, saying: "From the outset he trusted me, knowing that I shared fully his high ideals of business integrity and social responsibility. As my experience grew, his confidence in my judgment increased. Of that fact he gave abundant proof in the large gifts which he made me from time to time and which have enabled me with the passing years to continue in my own way to work for humanity throughout the world which he initiated and of which his own life and deeds were ever my example and inspiration."
JDR Jr. was associated with his father in the creation and development of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research (1901; now The Rockefeller University), the General Education Board (1902), The Rockefeller Foundation (1913), and the Laura Spelman Rockefeller Memorial (1918). He was on the Board of Trustees of The Rockefeller Institute from its beginning until 1954 and served as the board's president for twenty-one years. Upon his retirement as president in 1950, JDR Jr. said he always had regarded the institute as "the most significant and the most permanent of any that my father established." He served similar long terms as a trustee and as chairman of the General Education Board and of the Rockefeller Foundation.
THE BUREAU OF SOCIAL HYGIENE
One of his early activities in the field of social research grew out of his service as foreman of a Special Grand Jury in Manhattan which in 1910 investigated the white-slave traffic. The Grand Jury's much-publicized work led him to establish the Bureau of Social Hygiene in 1913. The Bureau, to which he contributed $5,400,000, carried out intensive studies of delinquency and crime and published a notable series of books over a number of years before it was dissolved in 1940.
WAR WORK
Throughout both World Wars, JDR Jr. devoted his energies to war work. He traveled the country during World War I speaking to audiences of soldiers in military camps and talking privately with men wanting advice and counsel. He also served as chairman of the United War Work Campaign in New York, which raised $35,000,000 for the various private organizations that were working with the troops. In 1941, before Pearl Harbor, he helped to establish the United Service Organizations (USO) and was an active leader of it. Two years later he joined in the formation of the National War Fund, including the USO, and served on its board. This Fund raised more than $321,000,000 to help the men and women of the armed forces, the merchant marine, and others.
JDR JR.'S CREED
During this period, JDR Jr. expressed in one concise statement his philosophy of life. On July 8, 1941, in a radio broadcast appeal on behalf of the USO and the National War Fund, he gave this statement of principles that was widely reprinted under the title, "I Believe":
I Believe
I believe in the supreme worth of the individual and in his right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
I believe that every right implies a responsibility; every opportunity, an obligation; every possession, a duty.
I believe that the law was made for man and not man for the law; that government is the servant of the people and not their master.
I believe in the dignity of labor, whether with head or hand; that the world owes no man a living but that it owes every man an opportunity to make a living.
I believe that thrift is essential to well ordered living and that economy is a prime requisite of a sound financial structure, whether in government, business or personal affairs.
I believe that truth and justice are fundamental to an enduring social order.
I believe in the sacredness of a promise, that a man's word should be as good as his bond; that character -- not wealth or power or position -- is of supreme worth.
I believe that the rendering of useful service is the common duty of mankind and that only in the purifying fire of sacrifice is the dross of selfishness consumed and the greatness of the human soul set free.
I believe in an all-wise and all-loving God, named by whatever name, and that the individual's highest fulfillment, greatest happiness, and widest usefulness are to be found in living in harmony with His will.
I believe that love is the greatest thing in the world; that it alone can overcome hate; that right can and will triumph over might. In 1962 these words were included on a commemorative plaque that honors him at Rockefeller Center.
BUSINESS ETHICS
In the years immediately following World War I, John D. Rockefeller, Jr. was a leader in the movement against the twelve-hour work day and the seven-day work week, which still prevailed in many industries. He said in a published statement in 1922 that working men and women should have better conditions because improved conditions represent the soundest economic policy and are "due the employee as a matter of common justice, required by the basic fact that man is a human being first and a member of industry afterward." In the same year, recognizing the need for basic research in the field, JDR Jr. organized Industrial Relations Counselors to make surveys for companies in which he had extensive holdings. The organization later undertook studies for other concerns and engaged in research in such subjects as unemployment insurance, pensions, and profit sharing.
JDR Jr.'s views on business ethics involved him in a stock proxy fight in 1929 that attracted world-wide attention. He had lost faith in the chairman of the board of the Standard Oil Company of Indiana, Col. Robert W. Stewart, because of what he regarded as Stewart's failure to respond frankly to questions put to him during a U.S. Senate Committee hearing. Rockefeller campaigned among the company's stockholders to remove Stewart as chairman, and he won. Even before the outcome of the proxy struggle was known, JDR Jr.'s position was generally applauded. The Chicago Tribune said on January 16, 1929:
"A generation can bring about astonishing changes. No one would have believed twenty-five or thirty years ago that a Rockefeller would ever have to appeal for public support to gain control of an oil company bearing the name 'standard,' or, indeed, of any oil company, whatever its name. No one would have believed that a Rockefeller would be engaged in such a struggle and fighting on the side of a more scrupulous business morality. That is what has happened; no one has said that Mr. Rockefeller is anything but sincere, and no one is likely to say it. Time and their own acts have softened public opinion toward the Rockefellers, father and son.
...In making the fight Mr. Rockefeller has served notice on all other men in all other companies in which he is interested that a business executive is responsible for something more than a good balance sheet. In addition, he has dramatized the issue of business morality and has concentrated attention upon it." RELIGION
All his life John D. Rockefeller, Jr. was deeply interested in matters relating to the Protestant church, and he was a leader in the interfaith movement. For many years he led the Young Men's Bible Class of the Fifth Avenue Baptist Church in New York, and he was honorary president of the Men's Class of its successor, the Riverside Church. He gave millions to the building of Riverside Church and for the Interchurch Center that serves as national headquarters of many Protestant and Orthodox church groups in the United States.
JDR Jr. deplored narrow denominationalism, and in many speeches and articles he urged the reuniting of Christendom. "Only a united Christian world can stem the rising tide of materialism, of selfishness, of shaken traditions, of crumbling moral standards, and point the way out," he said in a 1937 radio address. In 1955, he gave securities having a market value of approximately $20,000,000 to strengthen and develop Protestant theological education in the United States.
Out of his belief in the application of scientific methods in the religious field grew the Institute of Social and Religious Research, founded in 1921, to which he contributed $3,000,000. In its thirteen years of work, the Institute carried on research covering a wide range of topics including church organization, foreign missions, religious education, and race relations. He also gave $2,000,000 to strengthen Protestant theological schools in the younger church areas, especially Africa and Asia.
He was bound by no sectarian lines in his contributions to religious causes. Roman Catholic and Jewish organizations were among those receiving gifts.
A strict teetotaler himself, John D. Rockefeller, Jr. was nevertheless keenly sensitive to what was taking place in the country under Prohibition. When be became convinced that the 18th Amendment had not accomplished its objective, he wrote a highly publicized letter urging repeal of the amendment.
CONSERVATION
One of his deep interests was the conservation of natural resources. He traveled extensively across the U.S. in an intimate personal study of recreational and conservation needs. To the Acadia National Park in Maine and related projects he gave $3,568,000. At a cost of $5,930,000 he built and turned over Fort Tryon Park to New York City. In this park he erected The Cloisters to house the collection of Gothic art which he had given to the Metropolitan Museum of Art. His gifts to this project totaled $15,741,000. To the Palisades Interstate Park Commission, a New York-New Jersey body operating a chain of parks on the Hudson's western shore, he contributed $10,255,000; to the Save-the-Redwoods League in California, $2,027,000; to the Shenandoah National Park, $164,000; to the Yosemite National Park, $1,646,000; to the Jackson Hole Preserve, $17,497,000; and to the Sakura Park in New York City, $336,000. His contributions also made possible the preservation or restoration of three historical sites in Westchester County, New York -- Philipsburg Manor; Sunnyside, the home of Washington Irving; and Van Cortlandt Manor -- which he united under the auspices of Sleepy Hollow Restorations, an organization that he established in 1951 (now Historic Hudson Valley).
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
John D. Rockefeller, Jr.'s deep interest in international relations was reflected by his many contributions directed to international causes. Perhaps most outstanding in this field was his gift of $8,515,000 in December, 1946, for the purchase of the land for the permanent home of the United Nations in New York. "It is my belief that this City affords an environment uniquely fitted to the task of the United Nations and that the people of New York would like to have the United Nations here permanently," he said in making this gift. "If this property can be useful to you in meeting the great responsibility entrusted to you by the people of the world, it will be a source of infinite satisfaction to me and my family."
Previously, JDR Jr. had given to the League of Nations its great library building in Geneva. He also built the International Houses for students in New York, Chicago, Berkeley (California) and Paris (France).
INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION BOARD
In 1923 JDR Jr. founded the International Education Board, to which he gave more than $21,000,000. The Board operated in the fields of the natural sciences, the humanities and agriculture, and one of its notable contributions was $1,390,000 toward the 200-inch telescope on Mount Palomar, California, which was dedicated in 1948. Additional contributions by other Rockefeller boards brought the total given to complete the work on the telescope to more than $6,500,000. The telescope was considered one of the greatest scientific instruments ever developed, and the New York Times observed that "no such amount has ever before been invested in a single plant for purely scientific research."
Other contributions by the International Education Board were $357,000 for the establishment of a faculty of mathematics at Göttingen; $283,000 for Niels Bohr's work on atomic structure at Copenhagen, an undertaking which resulted years later in helping to develop the atom bomb; and $3,238,000 for the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago.
UNITED NEGRO COLLEGE FUND
JDR Jr. had a continuing interest in improving educational facilities and opportunities for African-Americans. He became chairman of the advisory committee of the United Negro College Fund and worked to help meet the financial needs of the more than thirty accredited, private colleges which the Fund aided. He contributed $5,250,000 to the Fund.
OTHER PHILANTHROPIC GIFTS
John Ensor Harr and Peter J. Johnson, authors of The Rockefeller Century (1988), calculate that the largest portion of JDR Jr.'s charitable gifts went to general and operating foundations ($192.2 million), such as the International Education Board and the Rockefeller Brothers Fund; that $71.7 million went to churches and religious organizations; $63.3 million toward historic preservation and restorations in the U.S.; $58.4 million to colleges and universities in the U.S.; $44.4 million to parks and conservation; $35.1 to libraries and museums; $13.2 million to foreign universities and institutes; $12.1 million to various cultural organizations; $11.8 million to hospitals; $9.5 million to relief agencies; $2.5 million to French restorations; and $22.8 million to miscellaneous other charitable purposes.
Among his contributions over the years were 725 acres of land near Alpine, New Jersey, to the Boy Scout Federation of Greater New York, and 375 acres to the North Bergen (N.J.) County Council of Boy Scouts; the 610-acre Rockefeller estate at Lakewood, New Jersey, to Ocean County for park purposes; $5,000,000 to Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts; and $1,400,000 to aid education for nursing and the utilization of nursing services. He also contributed liberally to the American School of Classical Studies for excavation of the Agora and the reconstruction of the Stoa of Attolos, both in Athens; to the American Academy in Rome; to Lingnan University in China; to the building of an archaeological museum in Old Jerusalem; to St. Luke's International Hospital in Tokyo; to the Shakespeare Memorial Endowment at Stratford-on-Avon; and for the library of Imperial University in Tokyo. He gave $5,000,000 in 1949 toward the needs of the Harvard Graduate School of Business Administration.
To the Rockefeller Brothers Fund, a foundation established in 1940 by his five sons, JDR Jr. gave a total of $58,981,000. He also bequeathed one-half of his estate to the Fund.
He also made outlays of approximately $10,000,000 for experiments in housing that resulted from his keen interest in improving housing for people of modest means. Some of the projects he undertook served to popularize the garden-type of apartments. Among his housing projects were the Paul Laurence Dunbar Apartments in Harlem; the Van Tassel Apartments in North Tarrytown (now Sleepy Hollow), New York; the Lavoisier Apartments in Manhattan; the Thomas Garden Apartments in the Bronx; and the Forest Hill Estates in Cleveland, Ohio.
COLONIAL WILLIAMSBURG
The restoration of Colonial Williamsburg in Virginia interested JDR Jr. more than any other project in which he was involved. His interest began with the start of the restoration in 1926 and grew continually over the years. He provided $56,012,000 to Colonial Williamsburg and related projects.
His involvement in the project was rooted in the conviction that the tangible records of an historic past are of great importance to modern peoples. He had earlier contributed to the restoration, after World War I, of Rheims Cathedral in France and the rebuilding of Louvain University Library in Belgium, destroyed during the war, and to the restoration and conservation of Versailles and Fontainebleau in France. At Williamsburg, his purpose was to help inform the American people of their heritage by restoring and preserving for all time the most significant portions of one of the most historic cities of our colonial period.
Williamsburg had been Virginia's colonial capital and a city that ranked with Boston, New York and Philadelphia in its contributions to cultural and political thought. JDR Jr. set up an organization, Colonial Williamsburg, to recreate accurately the environment of the 18th-century town and to provide visitors with an understanding of the thought as well as the life of that era. He intended for the streets and greens of the restored Williamsburg to be laid out as nearly as possible as they were in the days of the colony's first greatness. Hundreds of 19th- and 20th-century buildings were removed from the restored area, and many buildings and gardens of colonial days were faithfully reconstructed on their original sites.
Williamsburg also is home to the Abby Aldrich Rockefeller Folk Art Collection, a collection of 19th-century art which the first Mrs. Rockefeller donated to Colonial Williamsburg. In 1953 JDR Jr. donated a restored building and an endowment to maintain the collection and operate the museum.
ROCKEFELLER CENTER
Next to Colonial Williamsburg, JDR Jr. probably gave more attention to the development of Rockefeller Center than to any other project. The story of how it came to be built is well known. In 1928, John D. Rockefeller, Jr. joined with others in a plan to acquire a site on which a new Metropolitan Opera House was to be built. He leased the major part of the land now occupied by Rockefeller Center from Columbia University and purchased the remainder of the land from other owners. The Depression came before building could start, however, and the plans for the new Opera House faded away. JDR Jr., committed to a long lease of the Columbia property, decided to create an international business and entertainment center.
The land was cleared of more than 200 brownstone houses and other antiquated buildings, and the first fourteen buildings of Rockefeller Center were erected between 1931 and 1940. On November 1, 1939, JDR Jr. drove the last rivet in the steel work of the United States Rubber Company Building, the final structure completed before the war. More than 75,000 people worked on the construction of the Center during those Depression years.
BROTHERHOOD: THE GUIDING IDEAL
It may be said that John D. Rockefeller, Jr.'s life was directed toward the ideal chiseled in stone over International House in New York: "That Brotherhood May Prevail." He pursued this ideal through all means -- race, religion, business, education, welfare and science. It permeated his most intimate community associations as well as the international ideal of the United Nations. His civic responsibility expressed itself in communal activities on all levels. He had a sense of stewardship toward the wealth that was his and this led him to work hard to determine the needs and opportunities that would further the ideal he had chosen. His financial contributions followed a clearly defined pattern of service and were accompanied by his intensive personal participation.
John D. Rockefeller, Jr.'s charitable gifts are estimated to have totaled $537 million. Combined with his father's charitable contributions of $540 million, his donations brought the total philanthropic work of the first two generations of the Rockefeller fortune to more than $1 billion in the century between 1860 and 1960.
[Prepared by the staff of the Rockefeller Family Office May 1960; revised October 1969; revised by the staff of The Rockefeller Archive Center for online publication in September 1997]
Copyright © The Rockefeller Archive Center.
| 1874 |
January 29, 1874
|
Cleveland, Cuyahoga County, Ohio, United States
|
|
| 1903 |
November 9, 1903
|
New York, New York, United States
|
|
| 1906 |
March 21, 1906
|
New York, New York, United States
|
|
| 1908 |
July 8, 1908
|
Bar Harbor, Hancock County, Maine, United States
|
|
| 1910 |
May 26, 1910
|
New York, New York, United States
|
|
| 1912 |
May 1, 1912
|
New York, New York, United States
|
|
| 1915 |
June 12, 1915
|
New York, New York, United States
|
|
| 1960 |
May 11, 1960
Age 86
|
Tucson, Pima County, Arizona, United States
|